This post is part of The Ultimate Guide to Back Pain Relief
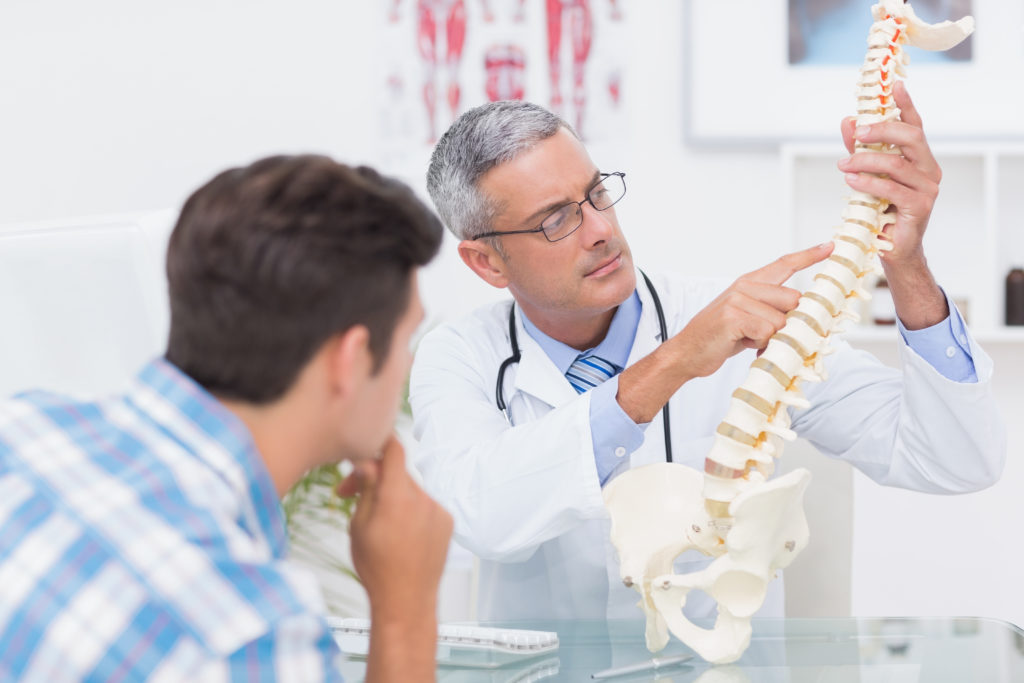
With so many treatment options for back pain, it can be hard to determine the best course of action. The first and most important step to treating your back pain is to understand the reason for your pain – getting the correct diagnosis. Not all back pain requires back surgery. In fact, a majority of back pain patients can use nonsurgical means and experience successful results. It all boils down to your specific condition and your treatment plan. In most cases, OrthoIndy spine surgeons will only consider back surgery an option when other medical and conservative treatment options have not provided enough improvement in patients’ symptoms.
What are some nonsurgical options for back pain?
For most people, back pain subsides relatively quickly without any formal treatment. Simply stopping the actions that are triggering your back pain helps. However, there are other options for treating your back pain:
- Medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as Aleve or ibuprofen are generally attempted. Additionally, a prescription for muscle relaxants or steroids are sometimes useful. Rarely, stronger pain medicines are considered.
- Heat or ice: Using a heating pad, cold pack or alternating between the two.
- Exercise: Although it’s best to avoid aggressive exercise after a back injury, using exercise to stretch your back and strengthen your core will help decrease back pain. A physical therapist can help determine the best exercise plan for your back pain. The plan includes a combination of strengthening, stretching and low-impact aerobic activity.
- Injections: A variety of injection options are available to help reduce pain, and are sometimes useful in figuring out what the exact cause of your pain is.
- Massage therapy: This can help reduce muscle stiffness and increase blood flow.
- Manual manipulation: In some cases, a chiropractor can decrease back pain by reducing pressure on sensitive structures, increasing flexibility, improving blood flow and reducing muscle tension.
- Stop smoking: Smoking leads to faster degeneration of the spine and increased back pain.
- Lose weight: Obesity has been linked to increased pain. Maintaining a healthy weight is always recommended and can have numerous other health benefits besides helping with back pain.
Use a personalized plan
Normally, if the pain does not improve over the course of three to four days, patients should consult with a non-operative spine care physician for further evaluation. Non-operative spine physicians differ from surgeons in that they do not perform surgery. The non-operative physicians utilizes medication management, physical therapy, and interventional procedures to treat pain and musculoskeletal injuries.
Patients seeking non-operative pain management care at OrthoIndy will be thoroughly evaluated with a physical examination, questioned about their past medical history and possibly examined with advanced medical imaging such as an MRI or X-ray. This information will be used to develop a treatment plan that may include non-operative care or in some cases a referral for a surgical consultation.
When is it time to consider back surgery?
A vast majority of patients do not require surgery. In most cases, surgery is considered only when non-operative treatments have not resulting in significant or lasting improvements. In these cases, you can review your case with an OrthoIndy spine surgeon to see whether you are a candidate to undergo surgery to try to accomplish your goals. Elective back surgery is your choice. Deciding on back surgery generally comes down to weighing the risks of undergoing the surgery with the expected benefits. Your surgeon will work with you to make sure you make an informed and educated decision.
Spine surgery generally involves treating one or more of the following:
- Nerve or spinal cord compression: When nerves or the spinal cord are compressed, it can result in pain, numbness, tingling, weakness, loss of coordination or balance, and even trouble with bowel or bladder function. During surgery, whatever is causing the compression is removed – which can include bone or bone spurs, disc material, ligaments, or cysts.
- Instability: Abnormal motion between the bones in your back can result from degeneration or ageing of the spine or sometimes from developmental defects in the bones. Fractures can often lead to instability of the spine. Finally, the surgeon may need to make the spine unstable in order to get pressure off of the nerves. When instability is present, a spinal fusion is generally needed to restore the stability to the spine.
- Spine deformities: When the spine loses its normal shape and results in scoliosis or kyphosis, surgery is sometimes used to restore the alignment of the spine. This also requires spine fusion to be performed to permanently hold the spine in its improved position.
Surgical emergencies
Surgical emergencies for back pain are extremely rare but they do occur. If you are experiencing a loss in bowel or bladder control or developing progressive weakness or numbness in the legs, these symptoms constitute a medical emergency and require immediate surgery. Please make an appointment with one of our spine surgeons right away.
You don’t need to live with back pain. There are solutions, both surgical and not. OrthoIndy spine physicians and spine surgeons work closely together to provide an optimal treatment course to help achieve your goals in the safest manner possible. Let OrthoIndy help you find a solution that works best for you.
Schedule an appointment
Your well-being is important to us. Click the button below or call us to schedule an appointment with one of our orthopedic specialists. If your injury or condition is recent, you can walk right into one of our OrthoIndy Urgent Care locations for immediate care. For rehabilitation and physical therapy, no referral is needed to see one of our physical therapists.

Get the Ultimate Guide to Back Pain Relief
Our comprehensive guide will help you understand back pain and its different causes, like sciatica, herniated disk, scoliosis, pinched nerves and more.