Introduction
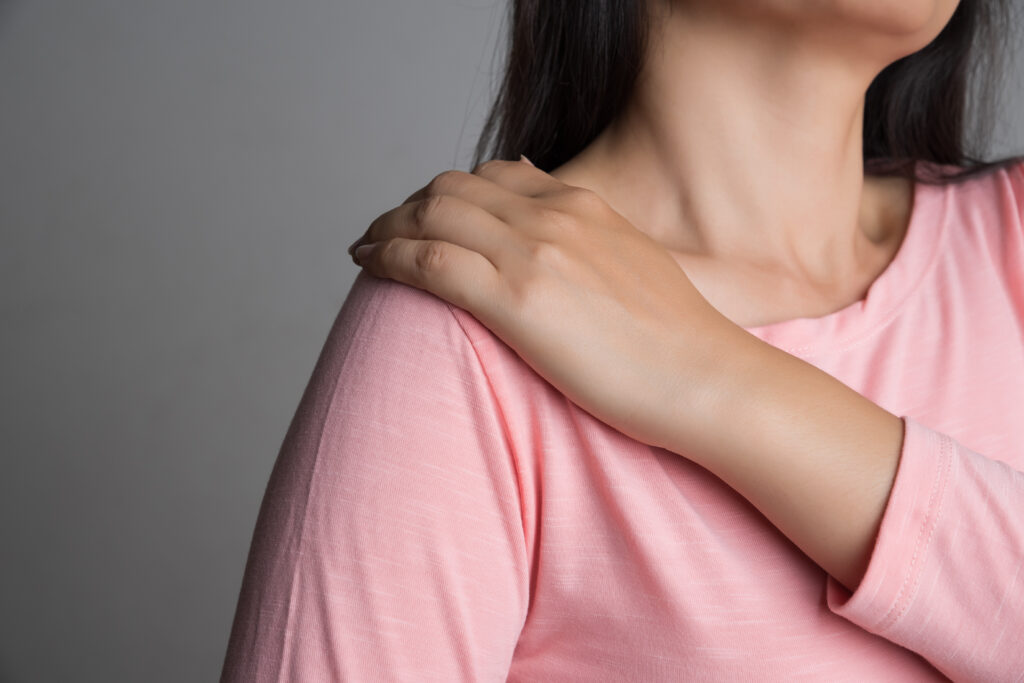
Shoulder impingement syndrome, also known as subacromial impingement, occurs when the tendons and bursas in the shoulder become compressed or irritated, resulting in pain and limited movement. This common condition often affects athletes and individuals who engage in repetitive overhead activities.
Causes
Several factors contribute to shoulder impingement syndrome:
- Repetitive Overhead Activities: Activities like swimming, throwing, or painting, which involve repetitive overhead movements, increase the risk of impingement.
- Poor Posture: Slouching or supporting poor posture alters the alignment of the shoulder joint, leading to impingement.
- Muscle Imbalances: Weakness or imbalances in the shoulder muscles disrupt normal joint mechanics, increasing the risk of impingement.
- Shoulder Instability: Compromised structures that stabilize the shoulder joint, such as ligaments or tendons, can contribute to impingement.
Symptoms
Shoulder impingement syndrome typically shows the following symptoms:
- Pain: Dull, aching shoulder pain, often extending down the arm, worsens with overhead movements or reaching behind the back.
- Limited Range of Motion: Impingement causes difficulty and discomfort when lifting the arm, reaching, or performing activities requiring full shoulder mobility.
- Weakness: Some individuals experience weakness in the affected shoulder, making it challenging to perform certain tasks.
Diagnosis
To diagnose shoulder impingement syndrome, a healthcare professional will conduct a thorough evaluation, including:
- Medical History: Inquiring about symptom onset, nature, and relevant medical conditions or earlier injuries.
- Physical Examination: Examining the shoulder for tenderness, swelling, or limited range of motion and performing specific tests to reproduce impingement symptoms.
- Imaging Tests: Ordering X-rays, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to assess the shoulder joint structures, rule out other causes, and evaluate the impingement extent.
Treatment
The treatment approach for shoulder impingement syndrome depends on symptom severity and underlying causes. Commonly recommended options include:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that worsen symptoms and supplying adequate shoulder rest for healing.
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in a structured program of stretching and strengthening exercises to correct muscle imbalances, improve posture, and restore proper shoulder mechanics.
- Pain Management: Prescribing non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Administering corticosteroid injections directly into the shoulder joint to reduce pain and inflammation in some cases.
- Surgical Intervention: Considering surgical intervention if conservative measures fail. The procedure typically involves removing or changing structures contributing to impingement, such as bone spurs or thickened bursa.
Prevention
To prevent shoulder impingement syndrome or reduce the risk of recurrence, consider the following measures:
- Maintain Good Posture: Practice proper posture during daily activities, particularly when working at a desk or performing repetitive movements.
- Strengthen Shoulder Muscles: Incorporate regular exercises to strengthen the shoulder muscles, improving stability and reducing the risk of impingement.
- Gradual Progression: When engaging in overhead activities or sports, gradually increase intensity and duration to allow the shoulder to adapt and prevent overuse injuries.
- Proper Technique: Learn and support correct technique and form for activities involving the shoulder joint, minimizing stress and strain.
- Regular Rest and Recovery: Allow sufficient rest and recovery time between activities to prevent overloading the shoulder joint and tissues.
Conclusion
Shoulder impingement syndrome is a common condition characterized by the compression or irritation of tendons and bursa in the shoulder joint. It often affects individuals involved in repetitive overhead activities or those with poor posture and muscle imbalances. The condition manifests through pain, limited range of motion, and weakness in the shoulder.
Diagnosis of shoulder impingement syndrome involves a thorough evaluation of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests to figure out the extent of impingement and rule out other potential causes of shoulder pain.
Treatment options for shoulder impingement syndrome include rest, activity modification, physical therapy, pain management with NSAIDs or corticosteroid injections, and, in severe cases, surgical intervention.
Prevention of shoulder impingement syndrome involves supporting good posture, strengthening the shoulder muscles, gradually progressing in activities, using proper technique, and allowing sufficient rest and recovery between activities.
If you experience persistent shoulder pain or suspect shoulder impingement syndrome, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for an exact diagnosis and proper treatment plan. Early intervention and proactive management can help alleviate symptoms, restore shoulder function, and prevent long-term complications.
Schedule an appointment
Your well-being is important to us. Click the button below or call us to schedule an appointment with one of our orthopedic specialists. If your injury or condition is recent, you can walk right into one of our OrthoIndy Urgent Care locations for immediate care. For rehabilitation and physical therapy, no referral is needed to see one of our physical therapists.