This post is part of the Ultimate Guide to Total Hip Replacement
A total hip replacement surgery may be necessary when the pain and function of your hip is not allowing you to have a great quality of life and non-surgical treatments are no longer helping you.
Anatomy
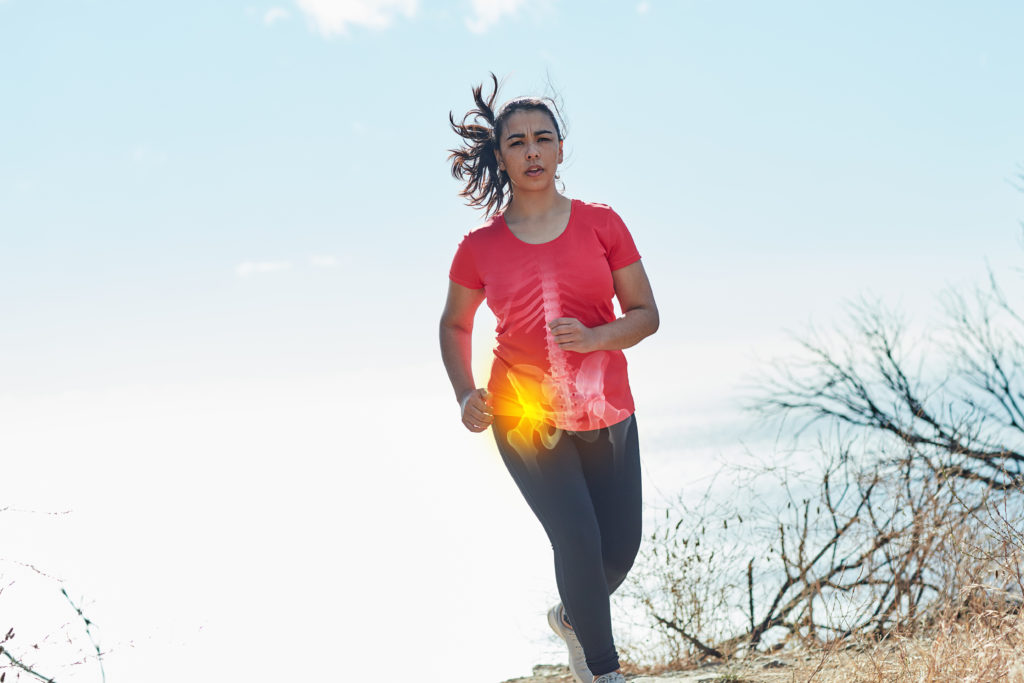
The hip is your body’s largest weight-bearing joint. This joint is also called a ball-and-socket joint. The ball is the upper end of the thigh bone (or femur), which fits into the socket (or acetabulum) at your pelvis. In a normal hip, cartilage covers the ends of these bones and cushions the hip joint for smooth, pain-free movement. When a hip is arthritic, the cartilage wears away, causing the bones to grind together. This produces pain and loss of motion.
Do I need a total hip replacement?
The most common cause of chronic hip pain and disability is arthritis. Most hip pain is caused by one of three kinds of arthritis: osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis or post-traumatic arthritis.
- Osteoarthritis: Mostly related to old age, it usually occurs in people over 50 years old, but can occur in younger people as well. The cartilage that cushions the bones of hip softens and wears away. The bones then rub against one another causing hip pain and stiffness. Osteoarthritis may also be caused or accelerated by subtle irregularities in how the hip developed during childhood.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: The synovial membrane that surrounds the joint becomes inflamed and thickened. This chronic inflammation damages the cartilage and eventually causes cartilage loss, pain and stiffness in the hip. This is the most common form of a group of disorders referred to as inflammatory arthritis.
- Post-traumatic arthritis: This can follow a serious hip injury or fracture. The cartilage may become damaged and lead to hip pain and stiffness overtime.
Additionally, an injury to the hip such as a dislocation or fracture, may limit the blood supply to the hip. This is called avascular necrosis. The lack of blood may cause the surface of the bone to collapse and arthritis will result. Some diseases can also cause avascular necrosis.
Childhood hip disease, where infants and children have hip problems, even if it is treated initially may still cause arthritis later on in life. This happens because the hip does not grow normally and the joint surfaces are affected.
Physician Examination
Your total joint surgeon will ask you for a complete medical history, ask questions about your pain and how long you have been experiencing it, and conduct a physical examination.An X-ray or MRI can confirm the best treatment options.
Make an appointment with a joint replacement specialist at OrthoIndy
How is a total hip replacement performed?
Total hip replacement surgery involves removing the diseased portion of the hip joint. An artificial hip, known as a prosthesis, replaces it. There are four pieces in a new hip implant: a stem which fits into your thigh bone, a ball on the end of the stem, a shell that fits into your pelvis and a liner that snaps into the shell. These come in many different sizes, like your own hip, and your total joint surgeon will custom fit your hip in the operating room.
Many hip implants function well for more than 15 years even in young and active patients. In addition to less invasive surgical techniques and improved implants, perioperative care and rapid rehabilitation is much different today than in the past. Today, the average length of stay after a total hip is one to two days in the hospital.
Some patients can even return home safely after an overnight, 23 hour stay. Early return to function is encouraged. Many total joint surgeons allow all activities except repetitive running and jumping. Overall, total hip replacement surgery is one of the most effective operations offered to patients today. It is reliable and durable and allows you to return to a better quality of life by decreasing your pain and improving your function.
How do you recover from a total hip replacement?
Following hip replacement, you will have a pillow between your legs while in bed to help decrease the chances of dislocating your hip. You will use an elevated commode and you will be taught how to get in and out of bed while obeying your hip precautions. Physical and occupational therapists will help you with your activities of daily living. This includes how to get to the bathroom, get dressed and go up and down steps using either a walker or crutches.
The whole goal is to help you become safe on your own so you can return home, even if you live alone; most of the time this is on the second day after surgery. They will also teach you a few exercises that you will continue to do after you leave the hospital.
You will do the exercises on your own. Pumping your ankles up and down is helpful in decreasing the chances of blood clots by keeping the blood moving in your legs. Tightening your thigh and buttock muscles is also helpful. You will have support stockings on both legs after surgery to help minimize swelling. Move around often after surgery.
Following hip replacement, you will obey the hip precautions for the first six weeks then we will show you how to bend over and pick things up, tie your shoes, etc. Otherwise, you simply go at your own speed as the hip rehabs itself as you continue to increase your activities.
Resumption of normal activities after joint replacement is highly dependent on the individual patient. The first two weeks are the most difficult.
General guidelines suggest around three weeks after surgery, most patients are driving a car and using a cane to walk. Most people are able to return to a sedentary type of job at five weeks and a more physically demanding job at seven weeks after surgery. You can work from home whenever you feel like it.
Your leg will be swollen after surgery. Travel is restricted to within two hours of home for the first month in order to decrease the risk of developing a blood clot in your leg. Many patients get back to activities such as walking for exercise, swimming, riding a bike and golfing by six weeks after surgery even though they still have some discomfort, increased warmth and increased swelling.
You will fatigue easily and will not sleep well for the first month after surgery, but this will improve with time. Patients are encouraged to increase your activities as you can tolerate. Don’t be afraid to push yourself. Many total joint surgeons ask their patients to avoid running and jumping activities after surgery as this can cause the implant to prematurely fail.
Learn more about joint replacement surgery at OrthoIndy.
Schedule an appointment
Your well-being is important to us. Click the button below or call us to schedule an appointment with one of our orthopedic specialists. If your injury or condition is recent, you can walk right into one of our OrthoIndy Urgent Care locations for immediate care. For rehabilitation and physical therapy, no referral is needed to see one of our physical therapists.