THIS POST IS PART OF THE ULTIMATE GUIDE TO FOOT AND ANKLE INJURIES
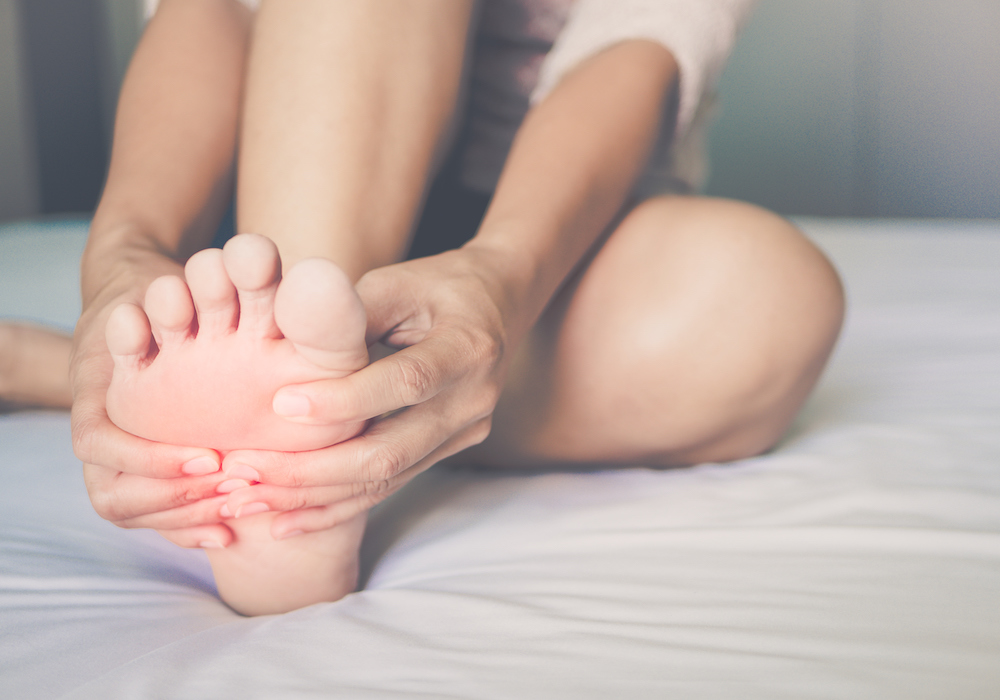
One of the most common problems of the foot and ankle, posterior tibial tendonitis or posterior tibial tendon dysfunction, occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed or torn. Left untreated, it can gradually result in flatfoot.
Anatomy
The posterior tibial tendon attaches the calf muscle to the bones on the inside of the foot. The main function of the tendon is to hold up the arch and support the foot when walking.
Cause
The posterior tibial tendon can tear due to overuse such as athletes who participate in high-impact sports including: basketball, tennis or soccer. An acute injury, such as a fall, can also cause posterior tibial tendonitis. Once the tendon becomes inflamed or torn, the arch will slowly fall over time.
Posterior tibial tendonitis is more common in women and in people over 40 years old. Obesity, diabetes and hypertension are additional risk factors related to posterior tibial tendonitis. This is the more common situation and usually develops with a clear injury.
Symptoms
- Pain along the inside of the foot and ankle
- Pain that is worse with activity
- Pain on the outside of the ankle
- Occasionally swelling will occur on the outside of the ankle
Physician examination
To determine whether you have posterior tibial tendonitis, your physician will ask you for a complete medical history, have you describe your symptoms and conduct a physical examination. An X-ray, CT scans or an MRI may be necessary to rule out other problems and confirm the diagnosis.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT WITH AN FOOT AND ANKLE SPECIALIST AT ORTHOINDY
What is the treatment for posterior tibial tendonitis?
In most cases, posterior tibial tendonitis is initially treated without surgery. Nonsurgical treatment options include: rest, ice, medication such as ibuprofen, immobilization, orthotics or braces. Pain may last longer than three months even with early treatment
Surgery is only necessary in cases when nonsurgical options have not provided relief after several months or if there is a tear of the tendon. Your physician will determine the best surgery option for you depending on where the tendonitis is located and how much the tendon is damaged.

Schedule an appointment
Your well-being is important to us. Click the button below or call us to schedule an appointment with one of our orthopedic specialists. If your injury or condition is recent, you can walk right into one of our OrthoIndy Urgent Care locations for immediate care. For rehabilitation and physical therapy, no appointment is needed to see one of our physical therapists.